The Impact of Greenhouse Construction Materials on Production Efficiency
01/12/2026
Hongqiangsheng
Greenhouses are an essential facility in modern agriculture, as they not only effectively extend the growing season of plants but also provide an ideal environment to promote plant growth. Choosing the right greenhouse construction materials is crucial for improving production efficiency. Different materials have their unique advantages and limitations, and understanding these characteristics can help agricultural producers maximize production efficiency, reduce operational costs, and achieve sustainable development. This article will explore the impact of greenhouse construction materials on production efficiency, focusing on the pros and cons of commonly used materials.
Classification of Greenhouse Construction Materials
Greenhouse construction materials can generally be divided into two categories: frame materials and covering materials. Each material performs differently in terms of stability, insulation, light transmission, and other factors, which directly influence the growing environment of crops.
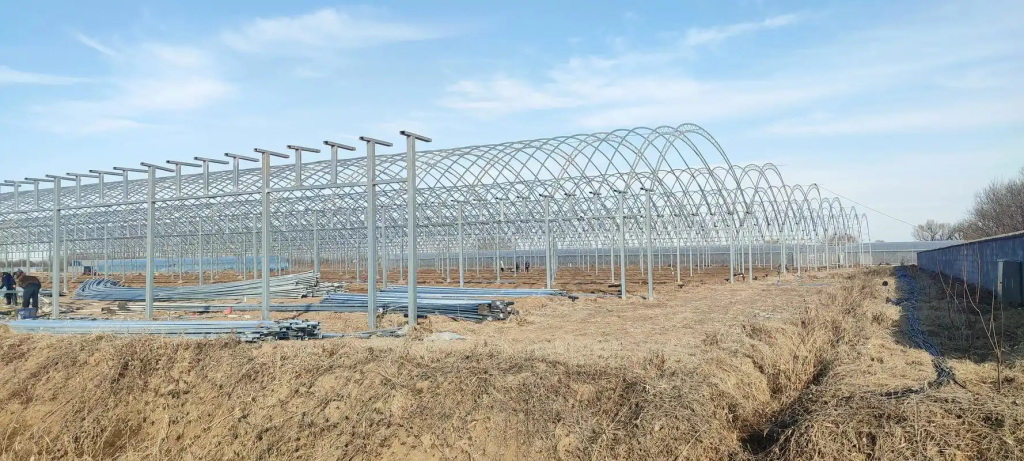

1. Frame Materials: Steel Structure
The frame materials of a greenhouse mainly determine its strength, durability, and ability to withstand wind and snow. Steel structure, as the preferred frame material, has several advantages:
-
High strength: Steel has very high strength and can withstand significant pressure and weight, making it suitable for large and multi-tiered greenhouses. Steel frame greenhouses can effectively handle strong winds and snow loads, maintaining the greenhouse’s stability.
-
Strong durability: Steel has a long service life, resists corrosion and damage, and reduces maintenance and replacement frequency. This is especially important in harsh climatic conditions, where steel structures are far more durable than wood or plastic frames.
-
Wind and snow resistance: Steel frame greenhouses can withstand strong winds and heavy snow pressure, making them ideal for areas prone to extreme weather conditions.
-
High load-bearing capacity: Steel structures provide sufficient support for internal greenhouse equipment (such as ventilation systems, heating systems, LED lighting, etc.), ensuring safe installation and allowing for the cultivation of more crops.
In summary, steel structure, as the frame material for greenhouses, offers significant advantages in terms of high strength, durability, and resistance to natural disasters, which are critical to enhancing greenhouse stability and production efficiency.
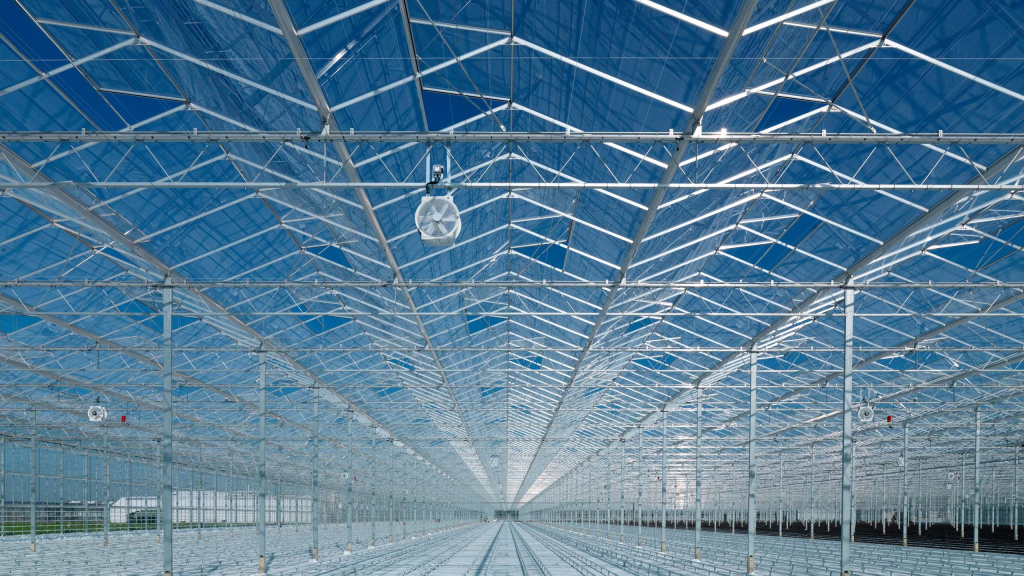
2. Covering Materials
Covering materials directly affect the temperature control, light intensity, humidity regulation, and other environmental factors within the greenhouse, thus influencing the growth rate and yield of crops.

-
Glass: Glass greenhouses are considered high-end greenhouses. Their advantages include high light transmission and excellent climate control. Glass has a light transmission rate of usually over 90%, which means plants can receive ample sunlight to support photosynthesis and promote growth. Additionally, glass is highly durable and wind-resistant, making it suitable for long-term investments. However, glass greenhouses are costly, and their thermal insulation is relatively poor, leading to high heating costs in winter.
-
Polycarbonate (PC): Polycarbonate, a transparent plastic material, offers high impact resistance and good insulation properties. Double or multi-layer polycarbonate panels are widely used as covering materials for greenhouses, improving insulation and reducing energy consumption while preventing excessive ultraviolet radiation, thus protecting plants from high temperatures and UV damage. Compared to glass, polycarbonate is more cost-effective and easier to install, making it ideal for medium and small greenhouses.

-
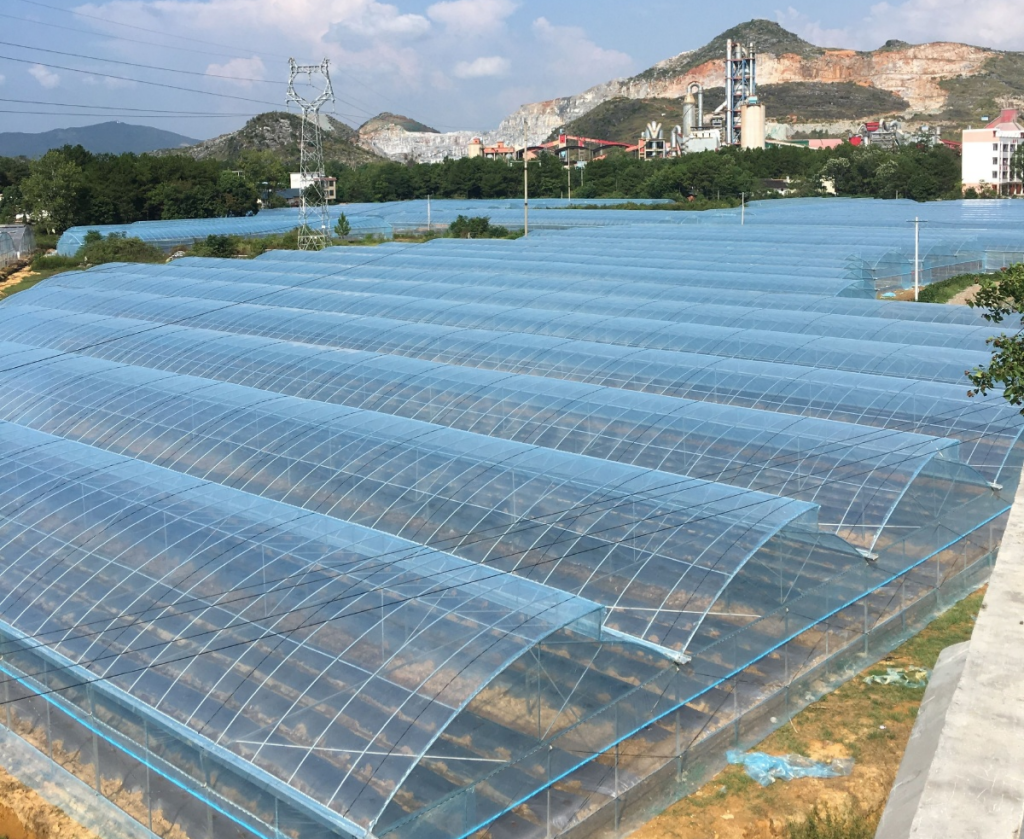
Plastic Films: Plastic film is one of the most common greenhouse covering materials, offering light weight and cost-effectiveness. Common types of plastic films include single-layer and double-layer films. Single-layer films are used for greenhouses in warm climates, while double-layer films provide better insulation and wind resistance. Although the light transmission rate of plastic films is lower than that of glass and polycarbonate, they still provide sufficient sunlight for plant growth. The main drawback of plastic films is their relatively short lifespan, requiring regular replacement, and their limited ability to resist UV radiation.
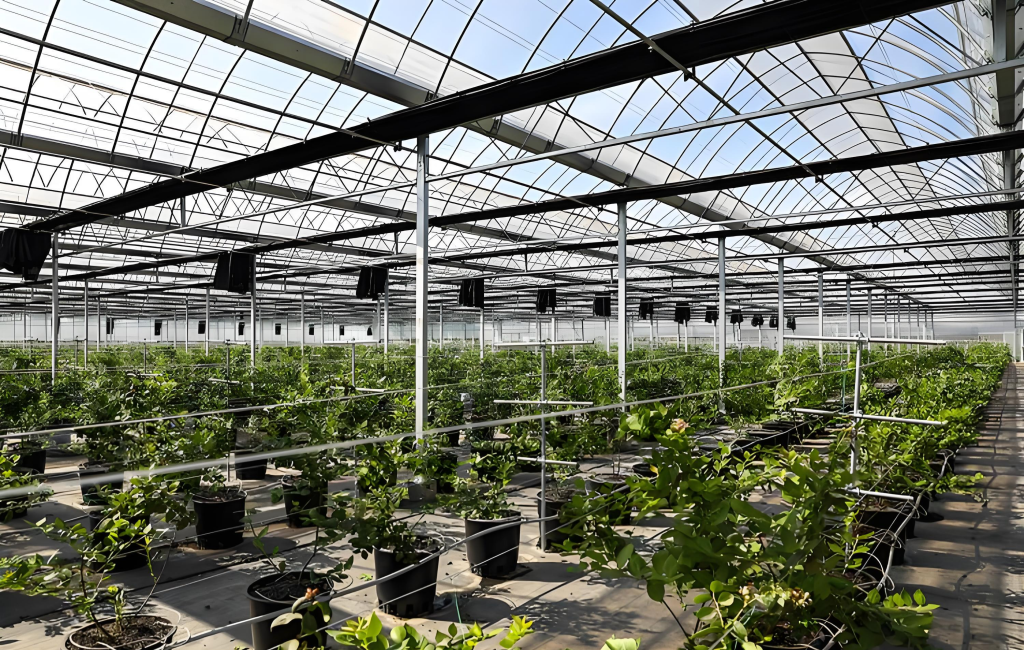

The Impact of Greenhouse Materials on Production Efficiency
The choice of greenhouse materials directly affects the growing environment, production efficiency, and costs of crops. The following are the key factors by which different materials influence production efficiency:
1. Temperature Control
Temperature is crucial for plant growth. Excessively high or low temperatures can inhibit plant growth. The insulation properties of covering materials directly impact temperature regulation inside the greenhouse. For example, polycarbonate and plastic films have better insulation properties, helping maintain stable indoor temperatures, which in turn improves crop growth efficiency. On the other hand, glass greenhouses have higher heat loss and may require additional heating systems to maintain temperature, increasing operational costs.
2. Light Intensity
Photosynthesis is the foundation of plant growth, and light intensity directly impacts the growth rate of crops. Glass and polycarbonate materials offer higher light transmission rates, benefiting photosynthesis and plant growth, making them suitable for crops with high light requirements. Plastic films have a lower light transmission rate but still provide sufficient light. In regions with abundant sunlight, however, plastic films may cause the greenhouse temperature to rise too high, affecting crop growth.
3. Energy Consumption
Energy consumption in a greenhouse directly impacts production efficiency and economic viability. By choosing appropriate construction materials, energy consumption can be reduced. For instance, polycarbonate and double-layer plastic films can effectively reduce heat loss, reducing the need for heating in winter and lowering energy costs. Glass greenhouses, on the other hand, typically require additional heating systems, resulting in higher energy consumption.
4. Durability and Maintenance Costs
The durability of different materials varies. Steel and polycarbonate materials have longer service lives, reducing the frequency of maintenance and replacement, thus lowering long-term costs. In contrast, plastic films and wood materials have shorter lifespans, requiring regular replacement or maintenance, which may affect the sustainability of production.
5. Adaptability and Flexibility
Different greenhouse construction materials are suited for different climate conditions and market needs. Steel structures and glass greenhouses offer greater adaptability to extreme climates or specific environmental requirements, handling harsh weather conditions such as strong winds and snow. Plastic films and wood are more suitable for warmer, drier climates, offering flexible and cost-effective construction options.
The choice of greenhouse construction materials plays a crucial role in agricultural production. Steel structures as the frame material provide strength, durability, and resistance to natural disasters, while the appropriate covering materials directly affect temperature, light, and humidity inside the greenhouse, impacting crop growth efficiency. Agricultural producers must consider factors such as production needs, climate conditions, budget, and long-term sustainability when selecting greenhouse materials to achieve maximum production efficiency and economic benefits. With the scientific and rational selection of materials, an optimal environment for agricultural production can be created, ultimately improving crop yield and quality.







