How to Save on Greenhouse Construction and Operating Costs Effectively
11/20/2025
Hongqiangsheng
In greenhouse agriculture, saving on construction and operating costs is an important concern for every farm owner and greenhouse operator. While greenhouse construction and operation can bring efficient production and stable profits, the initial investment and ongoing operating costs should not be overlooked. This article explores some effective strategies to save costs, helping you optimize greenhouse construction and operation and improve profitability.

1. Choose the Right Greenhouse Structure and Materials
The choice of greenhouse structure and materials directly impacts construction costs and long-term operating expenses. When designing and selecting a greenhouse, considering the following aspects can help save costs:
Greenhouse Structure: Choosing the right structure type (e.g., single-slope, double-slope, arch-shaped, underground greenhouse) can significantly reduce construction costs while ensuring good functionality. Simple yet sturdy frame structures are typically more cost-effective than complex designs.
Material Selection: Opting for cost-effective materials, such as polycarbonate sheets (PC sheets) instead of glass, can provide good insulation while being highly impact-resistant. Over the long term, this reduces maintenance costs. Additionally, greenhouse plastic films (e.g., PE films) are an affordable option, suitable for budget-conscious projects.
Wind Resistance Design: While reinforcing the wind resistance might increase initial investment, if your greenhouse is located in an area with high winds, having a wind-resistant design can help reduce losses due to wind damage, thus lowering future repair costs.
2. Utilize Natural Resources to Optimize Greenhouse Operation
The main operating costs for a greenhouse come from temperature regulation and water management. By utilizing natural resources to optimize these factors, you can significantly reduce energy consumption and water costs.
Solar Energy for Lighting and Heating: Utilizing solar energy is a core part of energy-saving in greenhouses. Choosing appropriate materials with high light transmittance (e.g., high-transparency films or double-layer polycarbonate sheets) increases natural light, reducing the need for artificial lighting and heating. Installing solar panels to provide renewable energy for the greenhouse not only reduces electricity costs but also contributes to a greener and more sustainable operation.
Natural Ventilation and Mechanical Ventilation: Using natural ventilation systems (e.g., opening windows, automated ventilation systems) can help maintain air circulation inside the greenhouse during the summer, reducing the need for air conditioning and fans, which saves energy. For colder seasons, you can use heating equipment like warm air heaters or air conditioning systems. Warm air heaters are more cost-effective for short-term heating needs, while air conditioning systems are suitable for precise and long-term temperature control, especially in areas with significant temperature fluctuations.
Rainwater Harvesting System: Installing a rainwater harvesting system to supplement irrigation water not only reduces water costs but also makes full use of local natural resources, minimizing reliance on groundwater or municipal water supplies.
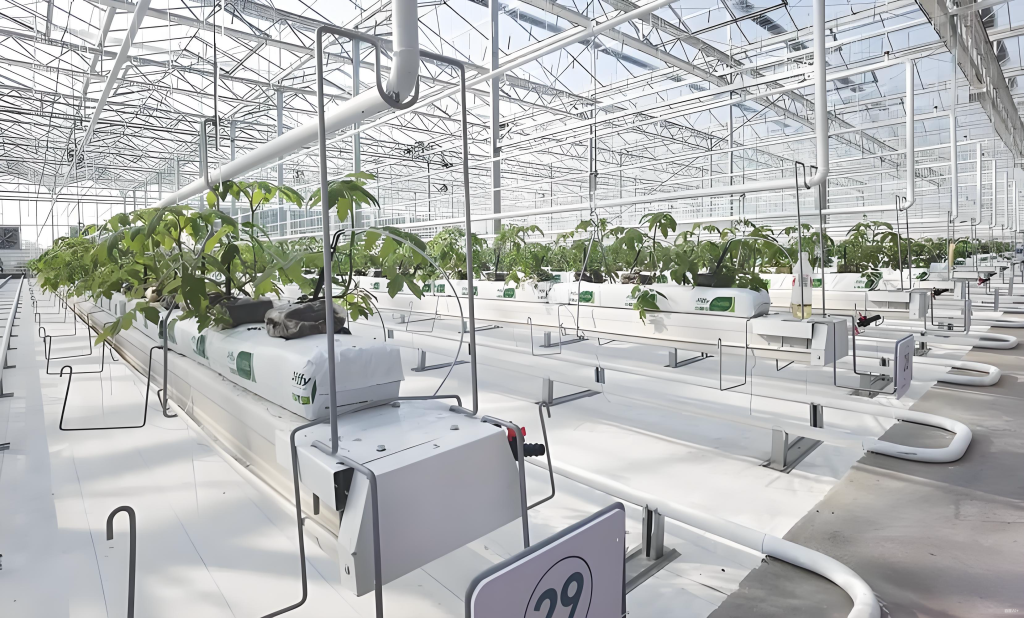

3. Invest in Automation and Smart Systems
Although automation and smart systems require higher initial investment, they can significantly reduce labor costs, increase production efficiency, and improve resource utilization in the long run.
Smart Temperature Control Systems: Installing smart temperature control systems allows for real-time monitoring of temperature, humidity, and light levels in the greenhouse. These systems can automatically adjust ventilation, heating, and lighting based on real-time data, ensuring optimal growing conditions while minimizing energy waste.
Automated Irrigation and Fertilizer Management Systems: Smart irrigation systems adjust water supply based on soil moisture levels, preventing overwatering and water wastage. Smart fertilization systems can precisely control the use of fertilizers, reducing unnecessary waste. This improves the efficiency of water and fertilizer usage while saving costs on these resources.

4. Optimize Labor Costs
Labor is another significant expense in greenhouse operations. By planning and managing labor effectively, you can reduce labor costs.
Training and Automation: Providing training for employees to operate automation equipment reduces errors and the need for manual labor. Automated equipment helps employees work more efficiently, reducing the time and cost associated with manual labor.
Streamlining Work Processes: By efficiently organizing work schedules and task assignments, unnecessary waiting times and repetitive tasks can be minimized, boosting employee productivity. For instance, during harvesting and sorting, automated harvesting equipment can reduce the time and cost of manual labor.

5. Save on Transportation and Logistics Costs
Transportation costs for greenhouse crops are a substantial part of agricultural operations. Here are a few ways to lower logistics expenses:
Bulk Purchasing and Shipping: By consolidating purchases of materials and shipping them in bulk, you can reduce the number of shipments and lower transportation costs. Collaborating with other greenhouse operators to share the costs of bulk procurement and distribution also reduces logistics costs.
Choose Local Suppliers: Opting for local suppliers for raw materials and equipment purchases reduces long-distance shipping costs. Establishing stable relationships with local suppliers also ensures faster delivery and more flexible after-sales service.

6. Regular Maintenance and Upkeep
Greenhouse equipment and facilities require regular maintenance and inspection to ensure long-term stable operation. While maintenance incurs some time and cost, timely inspection and upkeep can prevent excessive wear and tear, reducing repair and replacement costs.
Regular Inspections of the Greenhouse Structure: Regularly inspect the greenhouse frame and covering materials to ensure there are no cracks or damage. This helps avoid repair costs due to weather or external damage.
Maintenance of Automated Systems: Routine maintenance of automated systems, irrigation systems, ventilation systems, etc., prevents aging or malfunctioning equipment. Timely repair can avoid production stoppages due to equipment failure.

Saving on greenhouse construction and operating costs is not something that can be achieved overnight but is a result of careful planning, meticulous management, and technological innovation. Choosing cost-effective materials, utilizing natural resources, investing in automation, optimizing labor and logistics, and conducting regular maintenance are all effective ways to reduce costs. By adopting these strategies, you can not only increase the efficiency of greenhouse production but also remain competitive in the market and achieve long-term sustainable development.









